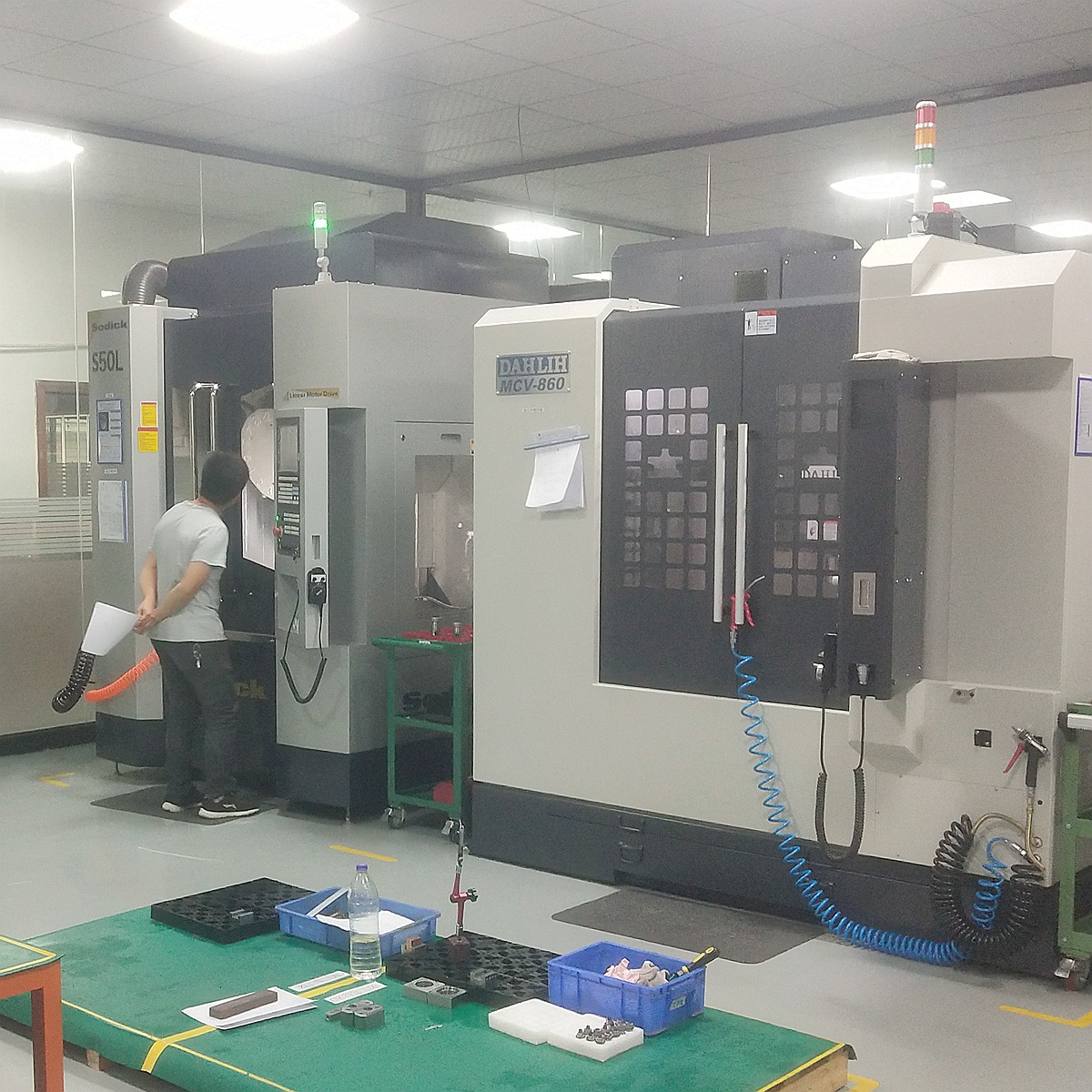
Choose the Right cNC Materials for Your Projects
Products
Contact
- jack@zhongyu-mould.com
- +86 180 2521 1913
- WhatsApp: 008618617251703
- Building 4, No.3 Zhaowuyi Road, Daning, Humen Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province.
Commonly used steel materials for injection molds and their properties
1. Pre-hardened Plastic Mold Steels (P20 / 718)
Common Grades: Chinese 3Cr2Mo (P20), Swedish 718 (improved type).
Key Properties: Supplied pre-hardened to HRC 30-35. They offer good machinability and polishability (can achieve over #3000 grit), combined with moderate strength and toughness.
Primary Applications: The workhorse steel for the vast majority of general-purpose plastic part molds, suitable for medium to large molds with production runs in the hundreds of thousands of cycles.
2. Through-hardened Mirror Polish Steels
Common Grades: S136 / 420SS (Corrosion-resistant), NAK80 (Precipitation-hardening).
Key Properties:
S136: A martensitic stainless steel. After quenching and tempering, it reaches a hardness of HRC 48-52. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and supreme mirror polishability (over #10000 grit), making it ideal for corrosive plastics like PVC and flame-retardant materials.
NAK80: Supplied pre-hardened to HRC 38-41, allowing direct machining. It achieves high hardness via precipitation hardening during aging, offers excellent polishability (mirror finish), and yields a smooth surface after EDM.
Primary Applications: Molds for transparent parts (lenses, light guides), high-gloss appliance surfaces, and corrosive plastics with the highest requirements.
3. High-Hardness, High-Wear-Resistance Steels (H13 / S7)
Common Grades: H13 (Hot-work tool steel), S7 (Shock-resistant cold-work steel).
Key Properties:
H13: After quenching and tempering, hardness reaches HRC 48-52. It possesses excellent hot strength, toughness, and thermal fatigue resistance, along with good thermal conductivity.
S7: Achieves high hardness after quenching (HRC 54-58) while maintaining exceptional toughness, capable of withstanding high impact.
Primary Applications: Molds for demanding conditions such as engineering plastics (e.g., PA+GF), highly abrasive materials, and rapid heat cycle molding (e.g., MuCell).
Core Selection Logic
Choosing mold steel is an exercise in balance:
Corrosion Resistance: Prioritize stainless steels like S136.
High Mirror Finish / Transparent Parts: Prioritize S136 or NAK80.
High Volume / Severe Abrasion: Choose high-hardness, wear-resistant steels like H13, often with surface treatments like nitriding.
Cost & Lead Time: P20/718 offers the best cost-performance for general applications.
The essence lies in a comprehensive trade-off based on plastic corrosiveness, production volume, surface quality requirements, and budget. Using inserts made from higher-performance steels for critical areas (like cores and gates) is also a common strategy to optimize overall cost-effectiveness.
