Choose the Right cNC Materials for Your Projects
Products
Contact
- jack@zhongyu-mould.com
- +86 180 2521 1913
- WhatsApp: 008618617251703
- Building 4, No.3 Zhaowuyi Road, Daning, Humen Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province.
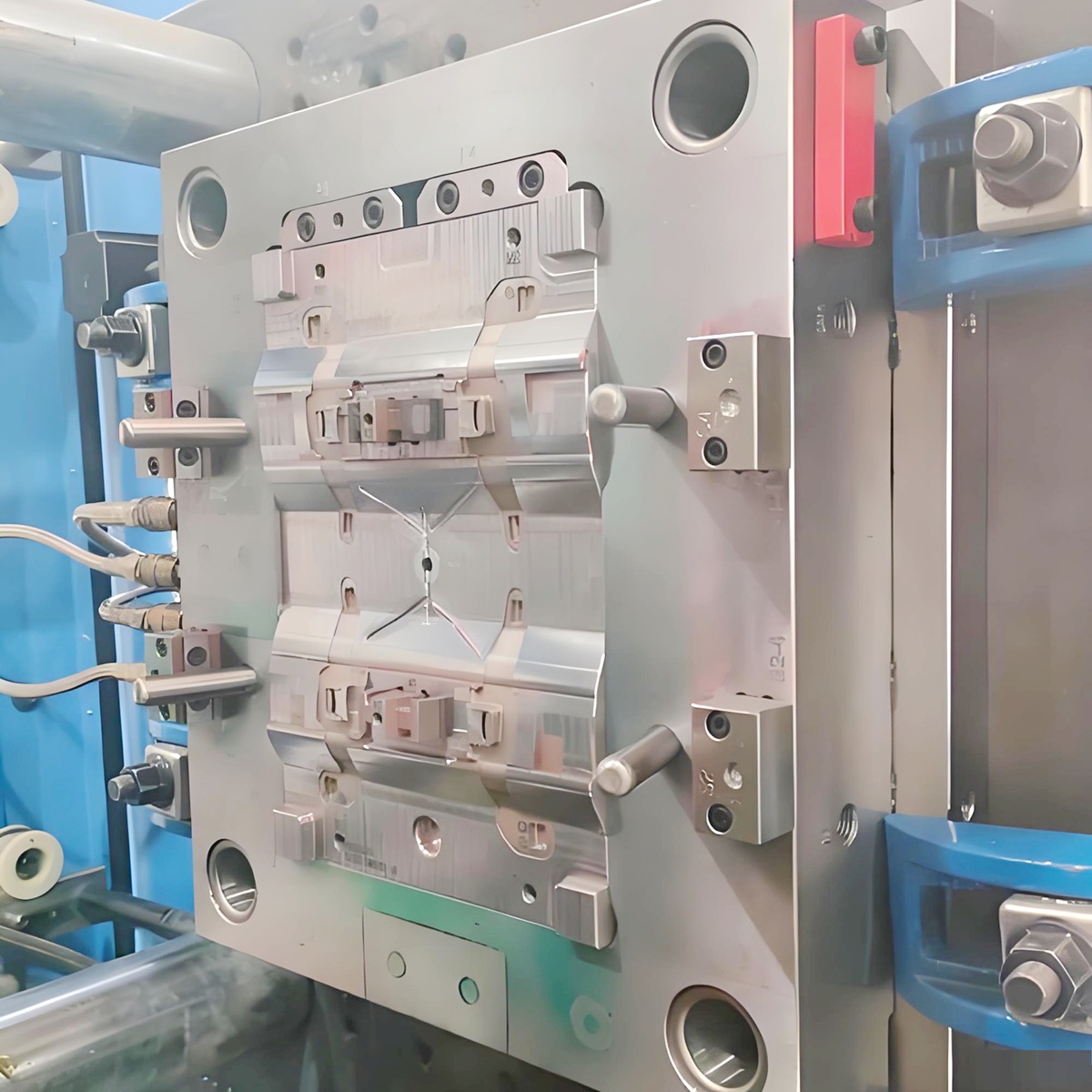
Precision Injection Molding Technology
Precision injection molding is an advanced manufacturing technology that achieves micron-level dimensional accuracy, nanometer-level surface roughness, and excellent functional consistency. Its core lies in the systematic control of the mold, process, and materials.
Key Technical Dimensions:
Ultra-Precision Mold Manufacturing and Temperature Control
Machining Accuracy: Key forming areas must achieve dimensional accuracy within ±0.003mm and surface roughness Ra < 0.05μm, relying on processes like mirror-finish EDM, 5-axis high-speed milling, and slow wire cutting.
High-Precision Temperature Control: Utilizes multi-circuit independent mold temperature control systems (water/oil temperature controllers) with a control accuracy of ±0.5°C, ensuring uniform cavity temperature distribution, which is crucial for controlling shrinkage and warpage.
Closed-Loop Precision Control of Process Parameters
Multi-Stage Injection: Divides the injection process into 4-6 phases, controlling speed and pressure separately to precisely manage filling behavior.
Precise Melt Management: Employs PID closed-loop control for screw temperature systems, combined with melt pressure/temperature sensors, enabling real-time feedback and adjustment of the melt state.
Application of Special Processes
Microcellular Foam Molding (MuCell): Injects supercritical fluid (e.g., N₂, CO₂) into the melt to form micron-sized bubbles, reducing warpage, shortening cycle time, and lowering weight while maintaining strength.
Stack Molds and High-Speed Molding: Doubles output through stack mold design; combined with servo-electric drives, enables ultra-high-speed mold opening/closing and injection.
Material and Design Synergy
Selects low-shrinkage, high-stability engineering plastics (e.g., LCP, PPS) and uses mold flow analysis (CAE) at the design stage to accurately predict and optimize filling, shrinkage, and cooling processes.
Core Value: Precision molding is not merely a competition in mold accuracy but a reflection of stability, repeatability, and system control capability. It is widely applied in high-end fields such as optical lenses, medical devices, and electronic connectors.
